For businesses that rely on external suppliers, the challenge of maintaining consistent quality is real. A supplier quality management system (SQMS) acts as the backbone, ensuring that all incoming materials meet rigorous standards and reducing the risk of costly errors. But implementing an SQMS isn’t just about compliance—it’s a strategic advantage that enables stronger partnerships, optimized processes, and ultimately, a more resilient business.
This blog explores how a modern SQMS can elevate supplier quality assurance, with actionable insights and best practices to help you get the most from your supplier relationships.
What Makes a Supplier Quality Management System Essential?
An effective supplier quality management system does more than just enforce standards. It fosters a proactive culture of quality, helping businesses stay agile in a competitive market. Here’s why an SQMS is indispensable:

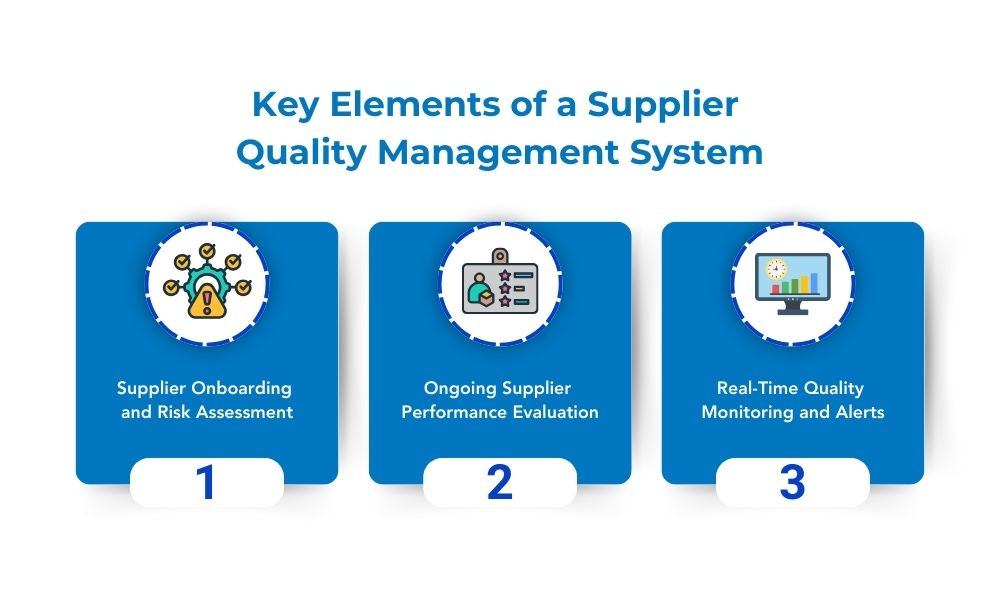
Key Elements of a Robust Supplier Quality Management System
To be effective, an SQMS needs several core elements that work in tandem. Each component serves a unique role in the quality assurance process:
Supplier Onboarding and Risk Assessment
Suppliers are the foundation of quality and onboarding them correctly is critical. A solid SQMS includes a rigorous assessment of new suppliers to ensure they align with your standards from day one.
- Background Checks: Assessing certifications, compliance records, and financial stability.
- Initial Risk Assessment: Evaluating potential risks associated with the supplier’s materials or processes.
- Clear Quality Benchmarks: Setting clear expectations and KPIs for new suppliers.
Ongoing Supplier Performance Evaluation
One-time audits aren’t enough in today’s fast-paced market. Continuous evaluation ensures that suppliers maintain quality standards over time.
- Performance Scorecards: Tracking metrics like defect rates, delivery accuracy, and responsiveness.
- Regular Check-Ins: Routine assessments and feedback loops to address issues proactively.
- Data-Driven Insights: Leveraging analytics to detect trends and areas for improvement.
Real-Time Quality Monitoring and Alerts
Automation and real-time tracking play an essential role in modern SQMS, allowing you to catch issues before they escalate.
- Automated Alerts: Notifying relevant teams when a quality threshold is breached.
- Compliance Dashboards: Providing an at-a-glance view of supplier status and compliance health.
- Integration with ERP Systems: Syncing quality data with enterprise systems for seamless tracking.
Supplier Quality Assurance Best Practices
To maximize the impact of an SQMS, it’s important to follow practices that promote transparency, accountability, and continuous improvement.
Clear Communication of Quality Expectations
When it comes to quality, ambiguity can be costly. Define quality standards and communicate them effectively to each supplier.
- Standardized Quality Documents: Including manuals, contracts, and SLAs.
- Regular Supplier Training: Ensuring suppliers are aligned with evolving standards.
- Transparency in Expectations: Using visual aids or scorecards to make requirements clear.
Risk-Based Supplier Segmentation
Not all suppliers carry the same risk, so it makes sense to segment them based on factors like product impact, compliance history, and risk level.
- High, Medium, and Low-Risk Segmentation: Prioritizing resources for high-risk suppliers while maintaining oversight for medium and low-risk ones.
- Customized Compliance Protocols: Tailoring audit frequency and quality checks based on risk.
- Strategic Partnerships: Building closer ties with critical suppliers who meet high-quality standards.
Collaboration and Feedback Loops
Supplier relationships thrive on open communication. A well-implemented SQMS fosters a culture of collaboration where feedback is two-way.
- Quarterly Performance Reviews: Using feedback sessions to address concerns and set new goals.
- Shared Scorecards: Allowing suppliers access to their quality data for self-monitoring.
- Continuous Improvement Projects: Partnering with suppliers on joint initiatives for quality enhancements.
Leveraging Technology for Supplier Quality Management
Modern SQMSs leverage technology to automate processes, enhance data accuracy, and streamline workflows, making quality management scalable and efficient.
Predictive Analytics for Proactive Quality Control
Predictive analytics can transform how you manage supplier quality by identifying trends before they result in non-conformances.
- Early Warning Signals: Identifying patterns that suggest potential risks.
- Data Visualization: Simplifying complex data sets to understand quality trends.
- Quality Forecasting: Projecting future supplier performance based on past data.
Cloud-Based Document Management
Cloud solutions allow for centralized document storage and easy access to compliance records, keeping everyone on the same page.
- Real-Time Document Access: Facilitating quicker decision-making.
- Version Control: Ensuring the most recent documents are always in use.
- Collaborative Platforms: Allowing suppliers and internal teams to work on the same document versions.

Conclusion
A well-implemented supplier quality management system is an asset that drives efficiency, builds stronger supplier relationships, and reduces risks across the supply chain. By focusing on quality assurance practices and embracing technology, businesses can achieve a proactive approach to supplier management. This proactive stance not only safeguards brand reputation but also ensures long-term growth and competitiveness.
A strategic, technology-driven SQMS like AsterDocs is more than a compliance requirement—it’s a foundation for a sustainable, quality-focused supply chain. For more information, visit our website today!













